Biodiversity
The variety of plants and animals found in a particular region is called the biodiversity of that region.
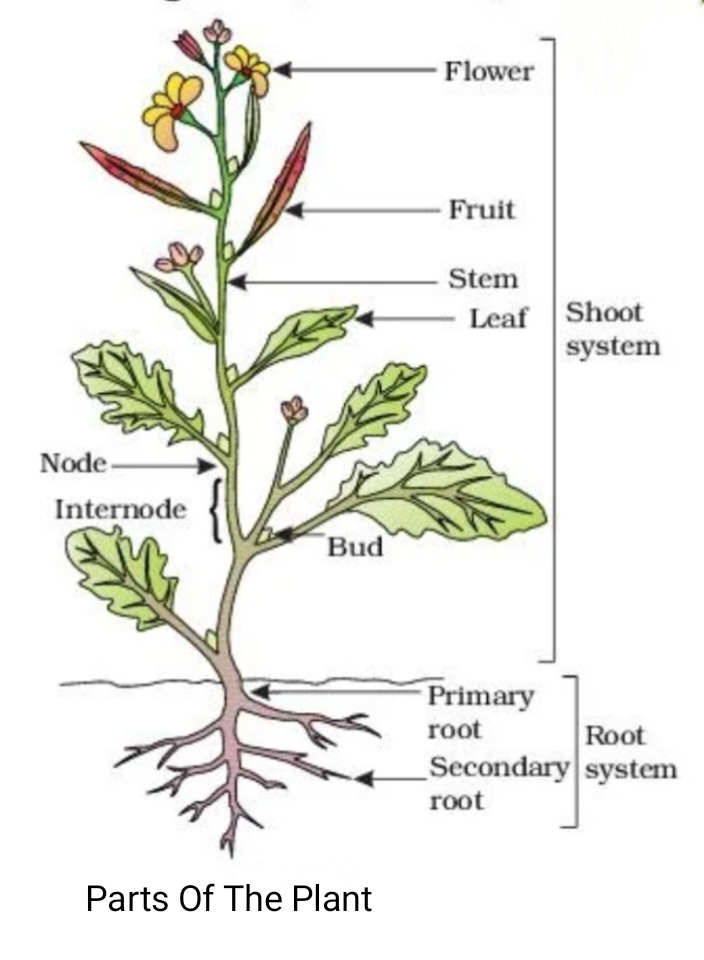
Types of the plants
The plants are of many types like trees, herbs, sherbs, climbers and creepers.
Trees
The plants which grow really big and tall with hard, thick, brown, and woody stems and have typical branches and stand higher up on the stem and away from the ground are called trees. For example, a mango tree, Peepal tree.
Shrub
The plants often have many hard, thin brown woody stems that start branching very close to the ground are called shrubs. These are not as tall as trees. For example, a rose plant is a shrub.
Herbs
The plants which are typically small with soft and green stem is called herbs.
Climbers
The plants with weak stems which need support and climbed on the trees for light to grow are called climbers.
Creepers
The plants of weak stems which creep along the ground and are called creepers.
There are variation in the shape and structure of these leaves.
Veins
The leaves of the plants have thin lines on it. These thin lines are called veins.
Venation
The pattern of veins on the leaf is called venation.
There are two types of venation on the leaves.
(i) Reticulate Venation
(ii) Parallel Venation
(i) Reticulate Venation
In some leaves, a net-like pattern of veins on both sides of a thick middle vein or mid rib is called reticulate venation.
For example, leaves of hibiscus exhibit reticulate venation.
(ii) Parallel Venation
In some leaves, veins run parallel to the middle vein or mid rib is called Parallel venation.
For example, the leaves of banana plants and grasses exhibit parallel venation.
Roots
Roots are the important underground part of all plants.
Taproot
The roots which consist of one main root and small secondry and tertiary roots arising from it is called taproot.
For example Mustard root and hibiscus
Fibrous Roots
The roots which appear as a bunch of similar-sized thin roots arising from the base of the stem of the plant are called fibrous roots.
For example: roots of common grass, maize
Types of the seeds
The parts inside the seed coat is called cotyledons. The seads are of two types according to the cotyledons.
(a) Dicot seed
(b) Monocot seed
(a) Dicotyledons or Dicot seed
The Plants that have seeds with two cotyledons are called dicotyledons or dicots. For example gramseed, ground nut seeds.
Dicot plants have reticulate venation and a taproot system.
(b) Monocotyledons or Monocot seed
The Plants that have seeds with one cotyledon are called monocotyledons or dicots. For example maze and ready seeds.
Monocot plants have parallel venation and a fibrous root system

Post a Comment
Post a Comment