Statistic–> The collection and presentation of data for interpretation is known as statistics.
सांख्यिकी –> आंकड़ों को इक्टूठा कर उनका विश्लेषण कर उनकी व्याख्या करने को सांख्यिकी कहते हैं।
Data –> Numerical figure are called data.
आंकडे –> संख्यात्मक रूप में प्राप्त अवलोकन समूह को आंकडे कहते हैं।
Range –> The difference between largest and lowest value or data is known as range.
Range = Highest value - Lowest value
परिसर –> उच्चतम व न्यूनतम आंकड़ों के बीच के अंतर को परिसर कहते हैं।
परिसर = उच्चतम आंकडा – न्यूनतम आंकडा
Tally Marks –> Symbols written in the form of vertical line '|' are called Tally Marks. Tally Marks are written like the following table.
मिलान चिन्ह –> खड़ी पाई '|' के रूप लिखे गये चिन्हों को मिलान चिन्ह कहते हैं। मिलान चिन्हों को निम्न सारणी के समान लिखते हैं।
Class and Class Intervals –> The numbers between which the observations are kept are called classes or class intervals.
वर्ग या वर्गअन्तराल –> प्रेक्षणों को जिन संख्याओं के मध्य रखा जाता है वर्ग या वर्ग अन्तराल कहलाते हैं।
Lower Limit and Upper Limit of the class–> Lower (least) number of the class is known as Lower Limit and upper (big) number of the class is known as Upper Limit.
Class Size (Class Limit) = Upper Limit – Lower Limit
वर्ग की उच्च सीमा व निम्न सीमा –> किसी वर्ग की छोटी या पहली संख्या को निम्न सीमा तथा बडी या दूसरी संख्या को उच्च सीमा कहते हैं।
वर्गन्तराल (वर्गामाप/वर्गसाईज) = उच्च सीमा – निम्न सीमा
Class mark –> The mid value of the class is known as class mark.
Upper Limit + Lower Limit
Class Mark = ___________________________
2
वर्ग चिन्ह –> किसी वर्ग के मध्य बिंदुओं को वर्ग चिन्ह कहते हैं।
उच्च सीमा + निम्न सीमा
वर्ग चिन्ह = ____________________
2
Frequency– > Number of the variable or observations written between a class sizes is known as frequency.
बारंबारता –> किसी वर्ग के मध्य लिखी संख्याओं को उस वर्ग की बारंबारता कहते हैं।
Mathematically Mean –> The average of all the numbers is known as Mathematically Mean of the data.
Sum of the Obsevation
Mathmetically mean = ________________________
Number of the Obsevation
अंक गणितीय माध्य –> सभी संख्याओं के माध्य औसत को अंक गणितीय माध्य कहते हैं।
सभी प्रेक्षणों का योग
मध्य (अंक गणितीय माध्य) = _____________________
प्रेक्षणों की संख्या (गिनती)
Mean –> The mean (or average) of a number of observations is the sum of the values of all the observations divided by the total number of observations. It is denoted by the symbol X. read as 'x bar'.
माध्य (या औसत) –> अनेक प्रेक्षणों का माध्य (या औसत) सभी प्रेक्षणों के मानों के योग को प्रेक्षणों की कुल संख्या से भाग देने पर प्राप्त होता है। इसे प्रतीक x से, जिसे X दंड (x bar) पढ़ा जाता है, से प्रकट किया जाता है।
Finding Median –> The data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order to find the median of ungrouped data.
आंकड़ों के माध्यक का परिकलन –> अवर्गीकृत आंकड़ों को आरोही (या अवरोही) क्रम में लिखने के उपरांत ही अवर्गीकृत आंकड़ों के माध्यक का परिकलन किया जाता है।
Median –> After arranging the ungrouped data into the ascending (or descending) order we will get the median.
The median is that value of the given number of observations, which divides it into exactly two parts.
(A) When the number of observations (n) is odd, then the median is the value of the
Me = [(n + 1)/2]th term
(B) When the number of observations (n) is even, Then the median is
माध्यक –> आंकड़ों को आरोही (या अवरोही) क्रम में लिखने के उपरांत अवर्गीकृत आंकड़ों के माध्यक का परिकलन किया जाता है
अतः माध्यक वह अवलोकन होता है जो दिए हुए प्रेक्षणों (आंकड़ों) को आरोही (या अवरोही) क्रम के ठीक-ठीक दो भागों में विभक्त कर देता है।
जब प्रेक्षणों की संख्या (1) विषम होती है, तब माध्यक होता है।
जब प्रेक्षणों की संख्या सम होती तब माध्यक है,
Me =
Mode –> An observation with maximum frequency is called the mode.
An observation with maximum frequency is called the mode. Here 'x' occurs most frequently, i.e., 'n' times. So, the mode is 'x'.
वें प्रेक्षण का मान होता है।
बहुलक –> यह वर्ग जिसकी वारंवारता सबसे अधिक होती है। उस वर्ग को बहुलक कहते हैं।
यह वर्ग जिसकी बारंबारता सबसे अधिक होती है। उस वर्ग को बहुलक कहते हैं। यहाँ 'X' आँकड़ा सबसे अधिक 'n' बार आया है। अतः, बहुलक 'X' है।




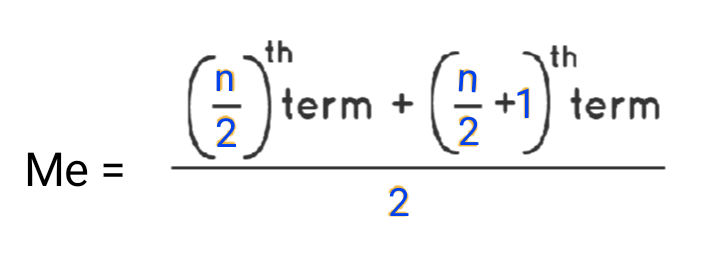
Post a Comment
Post a Comment