The word "Decimal" really means "based on 10" (From Latin decima: a tenth part).
We sometimes say "decimal" when we mean anything to do with our numbering system, but a "Decimal Number" usually means there is a Decimal Point.
Decimal Fraction
Or we can think of a decimal number as a Decimal Fraction.
A Decimal Fraction is a fraction where the denominator (the bottom number) is a number such as 10, 100, 1000, etc (in other words a power of ten)
What are Decimals?
In Algebra, decimals are one of the types of numbers, which has a whole number and the fractional part separated by a decimal point. The dot present between the whole number and fractions part is called the decimal point. For example, 34.5 is a decimal number.
Here, 34 is a whole number part and 5 is the fractional part.
“.” is the decimal point.
Let us discuss some other examples.
Here is the number “thirty-four and seven-tenths” written as a decimal number:

The decimal point goes between Ones and Tenths
34.7 has 3 Tens, 4 Ones and 7 Tenths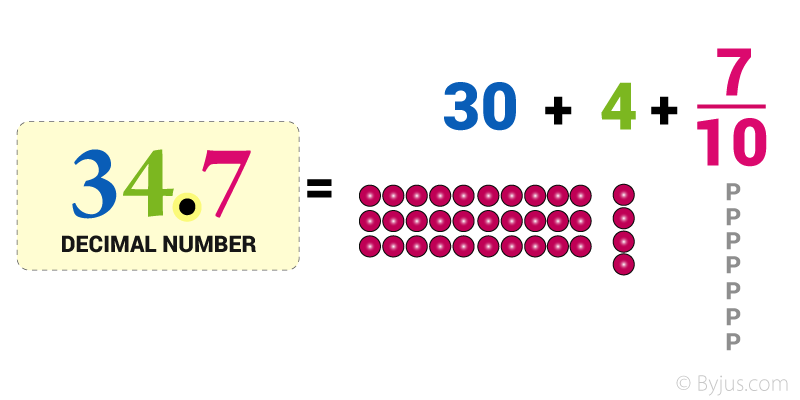
Types of Decimal Numbers
Decimal Numbers may be of different kinds, namely
Recurring Decimal Numbers (Repeating or Non-Terminating Decimals)
Example-
3.125125 (Finite)
3.121212121212….. (Infinite)
Non-Recurring Decimal Numbers (Non Repeating or Terminating Decimals):
Example:
3.2376 (Finite)
3.137654….(Infinite)
Decimal Fraction- It represents the fraction whose denominator in powers of ten.
Example:
81.75 = 8175/100
32.425 = 32425/1000
Converting the Decimal Number into Decimal Fraction:
For the decimal point place “1” in the denominator and remove the decimal point.
“1” is followed by a number of zeros equal to the number of digits following the decimal point.
For Example:
8 1 . 7 5
↓ ↓ ↓
1 0 0
81.75 = 8175/100
8 represents the power of 101 that is the tenths position.
1 represents the power of 100 that is the units position.
7 represents the power of 10-1 that is the one-tenths position.
5 represents the power of 10-2 that is the one-hundredths position.
So that is how each digit is represented by a particular power of 10 in the decimal number.
Place Value in Decimals
The place value system is used to define the position of a digit in a number which helps to determine its value. When we write specific numbers, the position of each digit is important.
Example:
For instance, let’s consider the number 456.
- The position of “6” is in One’s place, which means 6 ones (i.e. 6).
- The position of “5” is in the Ten’s place, which means 5 tens (i.e. fifty).
- The position of “4” is in the Hundred’s place, which means 4 hundred.
- As we go left, each position becomes ten times greater.
Hence, we read it as “Four hundred fifty-six”.

As we move left, each position is 10 times bigger!
Tens are 10 times bigger than Ones.
Hundreds are 10 times bigger than Tens.
And
Each time we move right every position becomes 10 times smaller from Hundred’s to Ten’s, to Ones
But if we continue past Ones?
What are 10 times smaller than Ones?
Before that, we should first put a decimal point,
So we already know that where we put that decimal point.

We say the above example as four hundred and fifty-six and eight-tenths but we usually just say four hundred and fifty-six point eight.
The power of 10 can be found using the following Place Value Chart:

The digits to the left of the decimal point are multiplied with the positive powers of ten in increasing order from right to left.
The digits to the right of the decimal point are multiplied with the negative powers of 10 in increasing order from left to right.
Following the same example 81.75
The decimal expansion of this is :
{(8*10)+(1*1)} + {(7*0.1)+(5*0.01)}
Where each number is multiplied by its associated power of ten.
Properties of Decimals
The important properties of decimal numbers under multiplication and division operations are as follows:
- If any two decimal numbers are multiplied in any order, the product remains the same.
- If a whole number and a decimal number are multiplied in any order, the product remains the same.
- If a decimal fraction is multiplied by 1, the product is the decimal fraction itself.
- If a decimal fraction is multiplied by 0, the product is zero (0).
- If a decimal number is divided by 1, the quotient is the decimal number.
- If a decimal number is divided by the same number, the quotient is 1.
- If 0 is divided by any decimal, the quotient is 0.
- The division of a decimal number by 0 is not possible, as the reciprocal of 0 does not exist.
Arithmetic Operation on Decimals
Like integers, the arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operation can be performed on decimal numbers. Now, let us discuss important tips while performing arithmetic operations.
Addition
While adding decimal numbers, line up the decimal points of the given numbers and add the numbers. If a decimal point is not visible (i.e., whole numbers), the decimal is behind the number.
Subtraction
Similar to the addition of decimal numbers, line up the decimal point of the given numbers, and subtract the values. To perform the arithmetic operation, use place holding zeros for our reference.
Multiplication
Multiply the given numbers like integers, as if the decimal point is not present. Find the product and count up how many numbers are present after the decimal point in both the numbers. The count represents how many numbers are required after the decimal point in the product value.
Division
To simply divide the decimal numbers, move the decimal point in the numbers such that the number becomes the whole numbers. Now, perform the division operation like the integer division.
| Related Links | |
| Decimals Word Problems | Square Root Of Decimals |
| Addition And Subtraction In Decimals | Application of Decimals in Daily Life |
Decimal to Fraction Conversion
The conversion of decimal to fraction or fraction to decimal values can be performed easily. Now, we will discuss both the conversion methods below:
Decimal to Fraction Conversion
We know the numbers after the decimal point represents the tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. Thus, while converting decimal to fraction, write down the decimal numbers in the expanded form and simplify the values
For example, 0.75
The expanded form of 0.75 is 75 x (1/100) = 75/100 = 3/4.
Fraction to Decimal Conversion
To convert the fraction to the decimal, simply divide the numerator by denominator.
For example, 7/2 is a fraction. If it’s divided, we get 3.5.
Decimal Problems
Example 1:
Convert 8/10 in decimal form.
Solution:
To convert fraction to decimal, divide 8 by 10, we get the decimal form.
Thus, 8/10 = 0.8
Hence, the decimal form of 8/10 is 0.8
Example 2:
Express 1.25 in fraction form.
Solution:
The given decimal number is 1.25
The expanded form of 1.25 is
= 125 x (1/100)
= 125 /100
=5/4
Hence, the equivalent fraction for 1.25 is 5/4.
Frequently Asked Questions on Decimals
What is meant by decimals?
Decimals are the numbers, which consist of two parts namely, a whole number part and a fractional part separated by a decimal point. For example, 12.5 is a decimal number.
What are the different types of decimals?
The two different types of decimals are:
Terminating decimals (or) Non-recurring decimals
Non-terminating decimals (or) Recurring decimals
How to convert fractions to decimals?
To convert fractions to decimals, divide the numerator by the denominator value.
Write the expanded form of 74.2?
The expanded form of 74. 2 is 70 + 4 + (2/10).
When do we use decimals?
The decimal numbers are used when the problem requires more precision than the whole value. For example, while dealing with weight, money, length, and so on.
To learn more about decimals, division of decimals, and operations of converting fractions to decimals, Register with BYJU’S, and strengthen your skills.
Given, 9.1, 3.22 and 0.66.
As we can see, 9.1 has only one digit after the decimal but 3.22 and 0.66 have two digits.
Hence, we can write 9.1 as 9.10
Now add all the three decimals.
9.10
+3.22
+0.66
——–
12.98
——
Click here to know about multiplying decimals.
Subtraction of decimals
Subtraction of decimals involves the subtraction of the decimal number with a small whole number part from the decimal number with a greater whole number part. However, we need to follow certain rules while performing the subtraction on decimals.
How to Subtract Decimals?
Subtraction of decimals is performed using the following steps:
Step 1: The numbers are first padded with zero depending upon the maximum digits present after the decimal for any of the numbers.
For example, while subtracting 3.456 from 7.1, since the number 3.456 has more digits after the decimal, the padding is done according to 3.456. Since 3.456 has 3 digits after the decimal, we pad 7.1 to three places as 7.100.
Step 2: The numbers are lined up vertically along with each other as shown below.

Step 3: Finally, subtract the decimal numbers similar to integers and place the decimal point accordingly.
Examples on Decimal Subtraction
Let us understand the concept more clearly with the help of the following examples:
Example 1: Subtraction: 7.304 – 1.15

Example 2: Subtraction 4.1 – 0.94
Practice Questions
Try solving the following practice problems to get a thorough understanding of the addition and subtraction of decimal numbers.
- Add the decimals: 84.956 and 210.28163.
- Subtract 54.12 from 64.2.
- Subtract 72.3261 from 80.
To learn more about the topic, download BYJU’S – The Learning App from Google Play Store and watch interactive videos. Also, take free tests to practice for exams.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is addition and subtraction of decimals?
How to do the addition of decimals?
Step 1: The numbers are first padded with zero depending upon the maximum digits present after the decimal for any of the numbers.
Step 2: The numbers are lined up vertically along with each other.
Step 3: Finally, add the decimal numbers similar to integers and place the decimal point accordingly.
How to do subtraction of decimals?
Step 1: The numbers are first padded with zero depending upon the maximum digits present after the decimal for any of the numbers.
Step 2: The numbers are lined up vertically along with each other.
Step 3: Finally, subtract the decimal numbers similar to integers and place the decimal point accordingly.
How do you line up decimal numbers in addition and subtraction?
How to subtract a decimal number from a whole number?
What is a Decimal?
We get decimals when we break a whole into smaller parts. A decimal number then has two components: a whole number part and a fractional part. The decimal place value system for the whole part of a decimal number is the same as the whole number value system. However, we get the fractional part of the decimal number as we move toward the right after the decimal point. The given image shows the decimal place value chart:
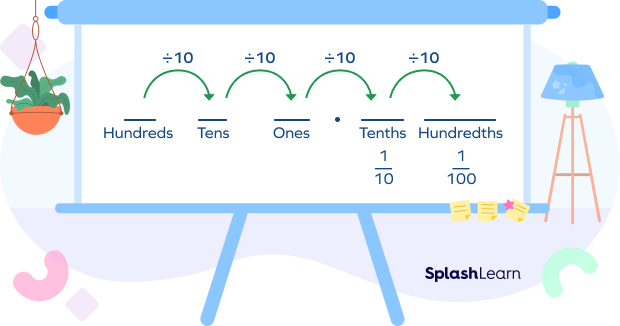
Note that as we go from left to right in the decimal place value system, each values is
The first place after the decimal point is called the “tenths”, which represents a place value of
Such fractions whose denominator is 10 or a positive power of 10 is called a decimal fraction.
The second place is called the “hundredths”, which represents a place value of
And the third place is called the “thousandths”, which represents a place value of
Here’s an example of a decimal number 17.48, in which 17 is the whole number, while 48 is the decimal part.



Post a Comment
Post a Comment