Triangles
Class 10
Ex 6.5
Q. 1. Sides of triangles are given below. Determine which of them are right triangles. In case of a right triangle, write the length of its hypotenuse.
(i) 7 cm, 24 cm, 25 cm
(ii) 3 cm, 8 cm, 6 cm
(iii) 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm
(iv) 13 cm, 12 cm, 5 cm
Solution:
(i) 25²= 7²+24²
625= 48+576
625=625
These sides of triangle formed right angle triangle with hypotenuse 25.
(ii) 8²= 3²+6²
64= 9+36
64 ≠ 45
These sides of triangle does not formed right angle triangle.
(iii) 100²= 50²+80²
10,000= 2500+6400
10,000 ≠ 8500
These sides of triangle does not formed right angle triangle.
(iv) 13²= 5²+12²
169= 25+144
169=169
These sides of triangle formed right angle triangle with hypotenuse 13.
Q. 2. PQR is a triangle right angled at P and M is a point on QR such that PM ⊥ QR. Show that PM2 = QM×MR.
Solution:
First Method:
In a right triangle perpendicular drawn from right angle to hypotenuse divides the triangle into two similar triangles.
ΔPQM∼ ΔRPM
ar ΔPQM/ar ΔRPM = PM²/RM²
[1/2×QM×PM]/[1/2×RM×PM]= PM²/RM²
PM²/RM² = QM/RM
PM = QM×RM
Second Method
In ΔPQR;
∠QPR=90° and
In ΔPQR and ΔMQP
In and
From and
Q. 3. In the given figure, ABD is a triangle right angled at A and AC ⊥ BD. Show that
(i) AB2 = BC.BD
(ii) AC2 = BC.DC
(iii) AD2 = BD.CD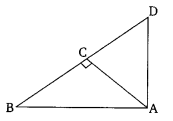
Solution:
Steps:
(i) In ΔBAD and ΔBCA
∠B = ∠B (Common Angles)
∠BAD = ∠BCA (90°)
(ii)

In ΔBAD and ΔBCA
∠B = ∠B (Common Angles)
∠BAD = ∠BCA (90°)
⇒ΔBAD ∼ ΔBCA (AA Similarity) ...(1)
In ΔABD and ΔACD
∠BAD = ∠DCA (90°)
⇒ΔBAD∼ΔBCA(AA Similarity)...(2)
From (1) and (2)
AC²=BC⋅CD
(iii)

In ΔABD and ΔACD
ty)
Q. 4. ABC is an isosceles triangle right angled at C. Prove that AB2 = 2AC2.
Solution:
Given:
In
∠ACB=90° and
But
(by Pythagorean Theorem)
Q. 5. ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. If AB2 = 2AC2 , Prove that ABC is a right triangle.
Solution:
Given:
In
And
Now,
is a right triangle
Q. 6. ABC is an equilateral triangle of side 2a. Find each of its altitudes.
Solution:
Given:
Sn equilateral triangle of side 2a.
So in
(because D is the midpoint of BC)
In ,
Units
Q. 7. Prove that the sum of the squares of the sides of a rhombus is equal to the sum of the squares of its diagonals.
Solution:
and OB = OD
To prove:
AB²+BC²+CD²+AD²=AC²+BD²
In rhombus
and OB = OD
In ∠AOB=90∘
⇒AB²=(½AC)²+(½BD)²
⇒AB²=¼AC²+¼BD²
⇒AB²=(AC²+BD²)/4
⇒4AB²= AC²+BD²
AB² + CB² + CD² + AD² = AC²+BD²
proved
Or
and OB = OD
To prove:
AB²+BC²+CD²+AD²=AC²+BD²
In rhombus
and OB = OD
In ∠AOB=90∘
Adding and
=2[(AC²/4+BD²/4+AC²/4+BD²/4)
= OC = AC/2 and OB = OD = BD/2
∴AB²+BC²+CD²+AD²=AC²+BD²
Q. 8. In the given figure, O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC, OD ⊥ BC, OE ⊥ AC and OF ⊥ AB. Show that
(i) OA2 + OB2 + OC2 – OD2 – OE2 – OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2
(ii) AF2 + BD2 + CE2 = AE2 + CD2 + BF2.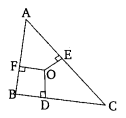
Solution:
Given:
(i) In ΔABC
OD⊥BC, OE⊥AC and
Construction;
and
In ΔOAF
Similarly, In ΔOBD
In ΔOCE
Adding and
(ii) From
[OA²+OB²+OC²−OD²−OE²−OF²] = AF²+BD²+CE²⋯(4)
[ are right triangles]
Q. 9. A ladder 10 m long reaches a window 8 m above the ground. ind the distance of the foot of the ladder from base of the wall.
Solution:
AB is height of the windows from the ground
is the length of the ladder
BC is the distance between foot and the ladder
Dince is right angled triangle
[Pythagoras Theorem]
BC²=10²−8²
BC²=100−64
BC² =36
BC=6m
The distance between foot of wall and the ladder is
Q. 10. A guy wire attached to a vertical pole of height 18 m is 24 m long and has a stake attached to the other end. How far from the base of the pole should the stake be driven so that the wire will be taut?
Solution:
Given:
The length of the pole B =18m
The length of the guy wire AC =24m
Distance between stake & pole = BC
In
∠ABC=90°
Q. 11. An aeroplane leaves an airport and flies due north at a speed of 1000 km per hour. At the same time, another aeroplane leaves the same airport and flies due west at a speed of 1200 km per hour. How far apart will be the two planes after 1
Solution:
is the distance travelled towards north
AB =1000km/hr×1½hr
AB = 1000×3/2km
AB = 1500km
The distance travelled by another aeroplane towards south
BC =1800km
Now, In ΔABC, ∠ABC =90°
The distance between two planes after 1½hr = 300√61km
Q. 12. Two poles of heights 6 m and 11m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between the feet of the poles is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
Solution:
The height of one pole AB
The height of another pole CD
Distance between poles bottom AC =12m
Distancebetween the tops of the poles D
Draw
Now consider,
In
Now,
The distance between the tops of poles
Q. 13. D and E are points on the sides CA and CB respectively of a triangle ABC right angled at C. Prove that AE2 + BD2 = AB2 + DE2.
Solution:
Steps:
Given: In ΔABC, ∠ABC=90∘
, are points on and
Construction:
Join , and
Proof:
In ,
In
Adding and

Steps:
Given: In ΔABC, ∠ABC=90∘
, are points on and
Construction:
Join , and
Proof:
In ,
In
InΔABC, ∠C=90∘
InΔCDE, ∠DCE = 90°
⇒DE ² = CD² + CE² .....(4)
Adding and
AE² + BD² = AB² + DE²
Q. 14 The perpendicular from A on side BC of a ∆ABC intersects BC at D such that DB = 3CD (see the figure). Prove that 2AB2 = 2AC2 + BC2.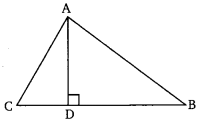
Solution:
Given: In
and BD=3CD
In RA ,
In RA ,
16
AB²=AC²+8BC²/16AB²
=AC²+½BC²
2AB²=2AC²+BC²
Q. 15. In an equilateral triangle ABC, D is a point on side BC, such that BD =
Solution:
Steps:
[ In an equilateral triangle perpendicular drawn from vertex to opposite side bisects the side]
Now In
[ is the height of an equilateral triangle which is equal to side]
AD²=7/9 BC²
Q. 16 In an equilateral triangle, prove that three times the square of one side is equal to four times the square of one of its altitudes.
Solution:
In
Now In
Chapter 6 Ex.6.5 Question 17
Q. 17 Tick the correct answer and justify : In , , and . The angle is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Solution ( c)
In
Pythagoras theorem is satisfied

















Post a Comment
Post a Comment