Ans. The living organisms are found in all over the Earth in snow, over the mountains, in water, on land and near the mouth of volcanoes too.
Q. What are common characteristics of living things?
Ans: Some common characteristics of living things are:
- Growth
- Movement
- Reproduction
- Respiration
- Excretion
- Stimuli
Q. What is growth?
Ans: The process of increase in shape, size and mass of the body or organs is called Growth.
Q. What is movement?
Ans: The process of changing of position or location from one place to another is called movement.
Q. Do animals move?
Ans: Yes, animals move from one place to another.
Q. Do plants also move?
Ans: Plants are generally fixed in the soil so they do not move from one place to another.
Ans: Producing of of their own kinds of young ones is called reproduction. All type of the reproduces.
Animals reproduce their own kind. The mode of reproduction may bedifferent, in different animals. Somea nimals produce their young ones through eggs. Some animals give birth to the young ones.
Plants also reproduce like animals.
Ans: The process in which oxygen is used by the living bodies into break down of food to get energy is called respiration. Water and carbon dixode is also produced in respiration.
Q. What is breathing?
Ans: The process of taking in oxygen and giving out carbon-dioxide (inhalation and exhalation of air) is called breathing. Breathing is a part of respiration process.
Q. What is excretion?
Ans: The process of removing of the waste materials of the body by the living organisms is known as excretion. Living organism excrete carbon dioxide, urine, sweat etc.
Q. Do plants also excrete?
Ans: Yes, plants also excrete in the form of rasin, carbon dioxide, oxygen, gum.
Some plants remove waste products as secretions which is collectied like gum.
Some plants cast their leaves to remove waste products deposits in leaves.
Q. What is stimuli?
Ans: The respond against the changes of our surroundings are called stimuli.
Q. How do you respond, if you suddenly step on a sharp object like a thorn, while walking barefoot?
Ans. Due to the stimuli, We remove our feet in seconds, if we suddenly step on a sharp object like a thorn, while walking barefoot.
Q. What happens? if you suddenly move from a dark place into bright sunlight.
Ans Due to the stimuli, our eyes will shut them selves automatically for a moment till they adjust to the changed bright surroundings. When we suddenly move from a dark place into bright sunlight.
Q. Why did wild animals run away when bright light is flashed towards them.
Ans. Due to the stimuli
Q. Why did cockroaches begin to move to their hiding places if the light in the kitchen is switched on at night.
Ans. Due to the stimuli
Q. Give some examples of responses of plants towards changes in their surroundings.
or
Q. Do plants also respond to stimuli?
Ans. Some examples of responses of plants towards changes in their surroundings are:
* Flowers of some plants bloom only at night.
* In some plants flowers close after sunset.
In some plants like Mimosa, (touch-me-not), leaves close or fold when someone touches them.
Q. What do you mean by the nutrition?
Ans. Nutrition:- Living organisms derive nutrients so they take food. Thus, the process of nutrition is the absorption of nutrients from raw materials or food.
Q. What do you mean by a habitat?
Ans: The place where organisms live and which provide food and safety for them is ‘called habitat.
Habitat means a dwelling place. The perticular place or surrounding where animals live is called their habitat. The habitat provides food, water, air, shelter and other needs to organisms.
So that we can say that the organisms depend on their habitat for their food, water, air, shelter and other needs.
Several kinds of plants and animals may live in the same habitat.
Q. What do you mean by a terrestrial habitats ? Give some examples?
Ans: The plants and animals that live on land are said to live in terrestrial habitats.
Some examples of terrestrial habitats are forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions.
Q. What do you mean by an aquatic habitats ? Give some examples?
Ans: The plants and animals that live in water are said to live in aquatic habitats.
Some examples of terrestrial habitats are Lakes, rivers and oceans are some examples of aquatic habitats.
Q. What do you mean by an Aerial habitats ? Give some examples?
Ans: The plants and animals that live in air are said to live in Aerial habitats.
Birds are the example of Arial habitat
Q. Give the Name of various types of habitat.
Ans:
(i) Terrestrial Habitats
(ii) Aquatic Habitats
(iii) Aerial Habitat
Q. Name few terrestrial habitats.
Ans: Deserts, mountains and grassland.
Q. Name some aquatic habitats.
Ans: Oceans, ponds and lakes.
Q. Name two aquatic animals.
Ans:
(i) Fish
(ii) Tortoise
Q. Name two terrestrial organisms.
Ans:
(i) Cat
(ii) Dog
Q. Name two examples of aerial habitat animals.
Ans:
(i) Birds
(ii) Mosquitoes
Q. What do you mean by the components of a habitat ? What are its type?
Ans: Things which find in a particular habitat for supporting to sustain life is called components of the habitat.
Components of habitat are of mainly two types:
(i) Biotic components
(ii) Abiotic components
Q. What do you mean by the biotic and abiotic components of the habitat?
Ans.
Biotic Components Of Habitat
The living components of a habitat is called Biotic Component Of Habitat.
The organisms, both plants and animals, living in a habitat are its biotic components.
Abiotic Components Of Habitat
The non-living components of a habitat is called Abiotic Component Of Habitat.
The non-living things such as rocks, soil, air and water in the habitat constitute its abiotic components.
Q. Give two examples of each biotic and abiotic components.
Ans: Plants and animals are biotic components, air and water are abiotic components.
Q. What are predators?
Ans: The animals which kill other animals for their food are called predators. For example a lion is a predators.
Q. What is a prey?
Ans: The animals which are killed by predators for their food are called prey. For example a deer or a rabbit is a prey.
Q. What do you mean by germination of seeds?
Or
Q. What is Germination?
Ans. The process of turning of a seed into a sprout is called germination. This type of the seeds are called sprouted or germinated seeds.
Germination is the beginning of life of a new plant.
Q. What do you mean by term adaptation?
Ans:
Q What do you mean by adoption?
Ans. Adaptation is the method by which organisms get well adjusted to the climate.
It is the presence of specific features or certain habits which enable an organism (plant or an animal) to live in its surroundings.
* Those organisms which cannot adapt to these changes die, and only the adapted oness urvive.
Q. Does adaptation take place in a short time?
Ans: No, adaptation does not take place in a short time, Because the abiotic factors of a region also change very slowly or change in thousands of years.
Q. Why did we find a wide variety of organisms in different habitats?
Ans. Organisms adapt to different abiotic factors in different ways. This results in a wide variety of organisms in different habitats.
Q. What do you mean by acclimatisation?
Ans: The small changes which take place in the body of a single organism over a short periods to overcome small problems due to changes in the surroundings are called acclimatisation.
Q. How the deserted animals like rats and snakes live in deserts which do not have long legs like a camel ?
Ans. The deserted animals like rats and snakes, which do not have long legs like a camel.
They stay away in deep burrows in the sand to escape from the intense heat.
These animals come out in search of food only during the night, when it is cooler.
Q. How the cactus plant is adapted to live in desert?
Or
Q. Write the features of desert plants.
Ans:
(i) The leaves in deserted plants are either absent or very small.
(ii) Leaves are converted into spines to reduce the loss of water by transpiration.
(iii) The stems become thick, flat and green which help in photosynthesis.
(iv) The stem is spongy and covered with waxy layer which helps to retain or stores water.
(v) The roots go very deep in the soil to absorb water.
Q. How the mountanious plant is adapted to live in mountain reasons?
Or
Q. Write the features of mountain reasons plants.
Class 6 Science Chapter 9 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Ans: Oaks, Pinus and Deodars.
4. Name two organisms that live in deserts.
Ans: Cactus, camel, desert rat.
5. Name a few plants that live in ponds.
Ans: Hydrilla, lotus, hyacinth etc.
Q. Name the habitats where various types of fishes live.
Ans: Pond, lake, river, sea.
Q. Name a common thing found in various types of fishes.
Ans: Streamlined body, fins, tail, Gills.
Q. Name the animal which is called the ship of desert.
Ans: Camel
Q. What is the function of gill? Name two aquatic animals which have no gills.
Ans: Gills help the fish to absorb oxygen dissolved in water.
Dolphin and whales have no gills.
Q. What are blowholes?
Ans: The organs by which dolphin or whales breathe are called blowholes or nostrills. These are located on the upper parts of their heads. They come out to the surface from time to time, to breathe in air.
Q. What is the main function of food?
Ans: Food gives energy to the organism which helps in growth, development and to do the work.
Q. What are the differences in the desert and sea regions?
Ans: In the sea, plants and animals are surrounded by salty water. Most of them use the air dissolved in water for breathing.
In desert, a very little amount of water is available. It is very hot in the day time and very cold at night. The organisms breathe air from the surroundings.
Q. Explain the features of fish which help it to adapt to live in water.
Ans:
(i) The shape of the fish is streamlined (boat like) which help in the movement.
(ii) They have flat fins and tails which help them to swim, change direction and to keep the body balanced.
(iii) They have gills which help in breathing in water.
(iv) The slippery scales/skin on their bodies to protect them.
Q. How are camels adapted to live in desert?
or
Q. Why did the camel called the ship of desert?
Ans: (i) The feet of the camels have thick, flat with large soles which help them in the movement on sand.
(ii) The long legs of camel helps to keep the body away from the heat of the sand.
(iii) When water is available, it drinks large amount of water at a time.They can live without water for a long time.
(iii) They release very little urine to prevent loss of water.
(iv) They release dry dung which also helps to prevent loss of water.
Q. Explain the adaptation of trees to live in mountain regions.
Ans:
(i) These trees are normally cone shaped.
(ii) They have sloping branches.
(iii) The leaves of some of these trees are needle-like.
(iv) These structures prevent accumulation of rainwater to slide off easily
(v) These structures prevent of staying snow over them and slide off easily.
Q. Explain the adaptation of animals to live in mountain region.
Ans:
(i) The animals have thick skin or fur to protect them from the cold surroundings like yak.
(ii) Some animals also have thick fur on their feet and toes which protect them from cold on walking in the snow like Snow leopard.
(iii) The goats have strong hooves for running up on rocky slopes like mountain goat.
Q. What is the work of root in terrestrial plants and aquatic plants?
Ans. In terrestrial plants, roots are modified and large which normally absorb the nutrients and water from the soil.
However, in aquatic plants, roots are much reduced in size and their main function is to hold the plant in place.
Q. Explain the adaptation of plants to live in water.
Ans:
(i) Roots are reduced in size which hold the plant.
(ii) Stems are long, hollow and light.
(iii) Stems grow up to the surface of water.
(iv) Leaves and flowers float on the surface of water.
(v) The leaves are covered by the waxy layer which protects the leaves from excessive water.
(vi) Some of the water plants have narrow and thin ribbon-like leaves. These can bend easily in the flowing water.
(vii) some submerged plants, leaves are often highly divided, through which the water can easily flow without damaging them.
12.What kind of movement do we see in plants?
Ans:
(i) Opening and closing of a flower.
(ii) Growth of a stem and leaves.
(iii) Movement of water, minerals and food from one part of the plant to other.
(iv) Movement of stem towards sunlight and root towards water in the soil.
Q. How the frog is adapted to live in land and water?
Q. Frogs can live both on land and in water, name the adaptations seen in these animals.
Ans: Frogs have strong back legs that help them in leaping and catching their prey.
They have webbed feet which help them to swim in water.
1.Explain the characteristics of living organisms.
Ans. There are following characteristics of living organisms
(i) All living organisms require food to maintain the life processes. This food gives energy for doing work, growth.
(ii) All living organisms show growth. Young ones of animals grow into adults. Plants also grow.
(iii) All living organisms respire. In respiration oxygen is used for the oxidftion of food and carbon dioxide is produced.
(iv) All living organisms respond to stimuli. All plants and animal respond to light, heat and the changes around them.
(v) All living organisms show excretion. The process of getting rid of waste product by the living organisms is called excretion. Plants also remove their wastes.
(vi) All living organisms reproduce. The process by which plants and animals produce their own kind is called reproduction.
Q.Write the difference between living and non-living things.
Ans.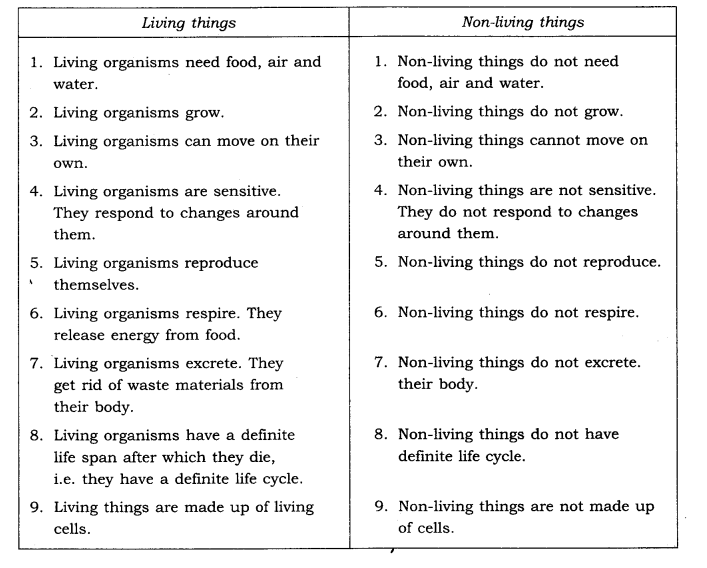
Summary Of The Book
* The surroundings where plants and animals live, is called their habitat.
* Several kinds of plants and animals may share the same habitat.
* The presence of specific features and habits, which enable a plant or an animal to live in a particular habitat, is called adaptation.
* There are many types of habitats, however, these may be broadly grouped as terrestrial (on the land) and aquatic (in water).
* There is a wide variety of organisms present in different habitats.
* Plants, animals and microorganisms together constitute biotic components.
* Rocks, soil, air, water, light and temperature are some of the abiotic components of our surroundings.
* Living things have certain common characteristics — they need food, they respire and, excrete, respond to their environment, reproduce, grow and show movement.
Exercise
Q. 1. What is a habitat?
Ans: The surroundings where animals live is called their habitat. The organisms depend on their habitat for their food, water, air, shelter and other needs. Habitat means a dwelling place.
Q. 2. How are cactus adapted to survive in a desert?
Ans: Cactus are adapted to survive in a desert as they have
(i) No leaves or spiny leaves to prevent water loss through transpiration.
(ii) Stem is modified in such a way that it performs photosynthesis and conserves water
(iii) Their roots go very deep into the soil for absorbing water.
Q. 3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The presence of specific features which enables a plant or an animal to live in a particular habitat is called___________ .
(b) The habitats of the plants and animals that live on land are called _________________ habitats.
(c)The habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called ____________________ habitats.
(d) Soil, water and air are the____________ factors of a habitats.
(e) Changes in our surroundings that make us respond to them are called
Ans:
(a) adaptation
(b) terrestrial
(c) aquatic
(d) abiotic
(e) stimuli
Q. 5. Give an example of a non-living thing which shows any two characteristics of living thing.
Ans: Example of non-living thing is cloud which shows following two characteristics of living things:
(i) It grows in size
(ii) It shows movement.
Butter, Leather, Soil, Wool, Electric Bulb, Cooking Oil, Salt, Apple, Rubber.
Ans: Butter, Leather, Wool, Cooking oil, Apple and Rubber are the non-living things which were once part of a living thing.
Q. 7. List the common characteristics of living things.
Ans: Some common characteristics of living things are:
- Growth
- Movement
- Reproduction
- Respiration
- Responsiveness
- Excretion
Q. 8. Explain why speed is important for survival in the grasslands for animals that live there. (Hint: There are few trees or places for animals to hide in grasslands habitats).
Ans: Speed is very important for survival of animals of grassland. In habitats of grasslands, there are few trees or places for animals to hide.
When their enemy attacks on them they have to run faster to reach a safe place.
If they fail to make. safe distance from predators, they lose their life. So, the speed is very important for survival of animals of grassland.
























Post a Comment
Post a Comment