Class 06 || Science || Ch. 10. Motion and Measurement of Distances
Q. How the transport developed? Draw a path of development of transport?
Ans. In ancient times people use animals cards and boards to carry loads.
After the inventionof steam engine led to the developmentof new means of transport. Railroads were made for steam engine driven carriages and wagons.
Later came automobiles such as motor cars, trucksand buses. Motorised boats and ships wereused as means of transport on water.
Electrictrains, monorail, supersonic aeroplanesand spacecraft are some of thecontributions of the 20th century.
The SI unit of length is a metre.
1m = 10dm = 100cm = 1000mm
1dm = 10cm = 100mm
1cm = 10mm
Exercise
Chapter 10 - Motion and Measurement of Distances
Q. 1. Give two examples each of modes of transport used on land, water, and air.
Ans. Examples of modes of transport used on
Land: Bus, car, train, truck
Water: Ship, boat, Steamer
Air: Aeroplane, helicopter
Q. 2. Fill in the blanks:
(i) One metre is __________ cm.
(ii) Five kilometres is __________ m.
(iii) Motion of a child on a swing is ___________.
(iv) Motion of the needle of a sewing machine is ___________.
(v) Motion of wheel of a bicycle is___________.
Answer.
(i) One metre is 100 cm.
(ii) Five kilometres is 5000 m.
(Explanation:
We know that 1 km = 1000 m
5 km = 1000 × 5
= 5000 m
(iii) Motion of a child on a swing is periodic.
(iv) Motion of the needle of a sewing machine is periodic.
(v) Motion of the wheel of a bicycle is circular motion.
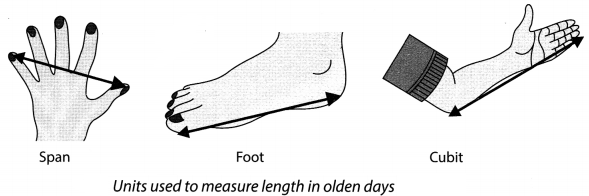
Q. 3. Why can a pace or a footstep not be used as a standard unit of length?
Ans. Because the size of pace or footstep of different people are different so the lengths measured by two different persons using their footsteps will not be the same. Due to this reason pace or a footstep cannot be used as a standard unit of length
Q. 4. Arrange the following lengths in their increasing magnitude:
1 metre, 1 centimetre, 1 kilometre, 1 millimetre
Ans.
1 m = 100 cm
1 cm = 10 mm
1 m = 100 × 10 = 1000mm
Now, 1 km = 1000 m
1 km = (1000 × 100)cm = 100000 cm = (100000 × 10)mm = 1000000mm
So, arranging 1 metre, 1 centimetre, 1 kilometre, 1 millimetre in increasing order we have:
1mm < 10mm < 1000mm < 1000000mm
Or 1 millimetre < 1 centimetre < 1 metre < 1 kilometre
Q. 5. The height of a person is 1.65 m. Express this in cm and mm.
Ans. Height of the person = 1.65 m
We know that 1 m = 100 cm
1.65 m = 100 × 1.65 = 165 cm
Again, 1 m = 100 cm = 1000 mm
1.65 m = 1.65 × 1000 = 1650 mm
Thus height of person in cm = 165 cm
And height of person in mm = 1650 mm
Q. 6. The distance between Radha’s home and her school is 3250 m. Express this distance in km.
Ans. The distance between Radha’s home and her school is 3250 m.
We know that 1 km = 1000 m
Or 1000 m = 1 km
Or 1m = 1/1000 Km
Thus, 3250 m = (1/1000) X 3250 = 3.25 Km
Therefore, distance between Radha’s home and her school in km = 3.25 km
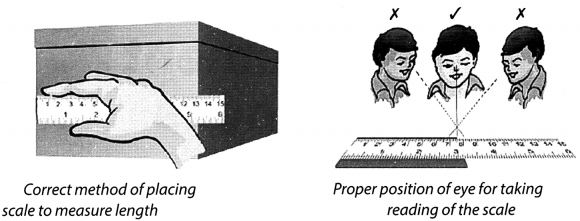
Q. 7. While measuring the length of a knitting needle, the reading of the scale at one end is 3 cm and at the other end is 33.1 cm. What is the length of the needle?
Ans. Length of the knitting needle is the difference between two readings.
Thus, length of knitting needle = 33.1− 3.0 = 30.1 cm
Q. 8. Write the similarities and the differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan that has been switched on.
Ans. Similarity between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan is that both the wheels of bicycle and the fan are moving around a fixed point and possess circular motion.
Differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan is that a bicycle has linear motion as it moves forward, whereas ceiling fan does not possess the linear motion.
Q. 9. Why can you not use an elastic measuring tape to measure distance? What would be some of the problems you would meet in telling someone about a distance you measured with an elastic tape?
Ans. Elastic tapes are stretchable. So, the length of an elastic measuring tape will change each time due to stretching. So, it will not give correct measurement of a distance. Therefore, we cannot use an elastic measuring tape to measure distance. While measuring the distance with an elastic tape, we will get different values of the same distance each time.
Q. 10. Give two examples of periodic motion.
Ans. Examples of periodic motion are: (any two)
Motion of a pendulum, Motion of a swing, Motion of Earth around the Sun, Motion of a rocking chair etc.











Post a Comment
Post a Comment